Part 2 Ip Subnet Masks Private And Public Ipv4 Addresses Classless Ip Addressing

Subnet Mask Class
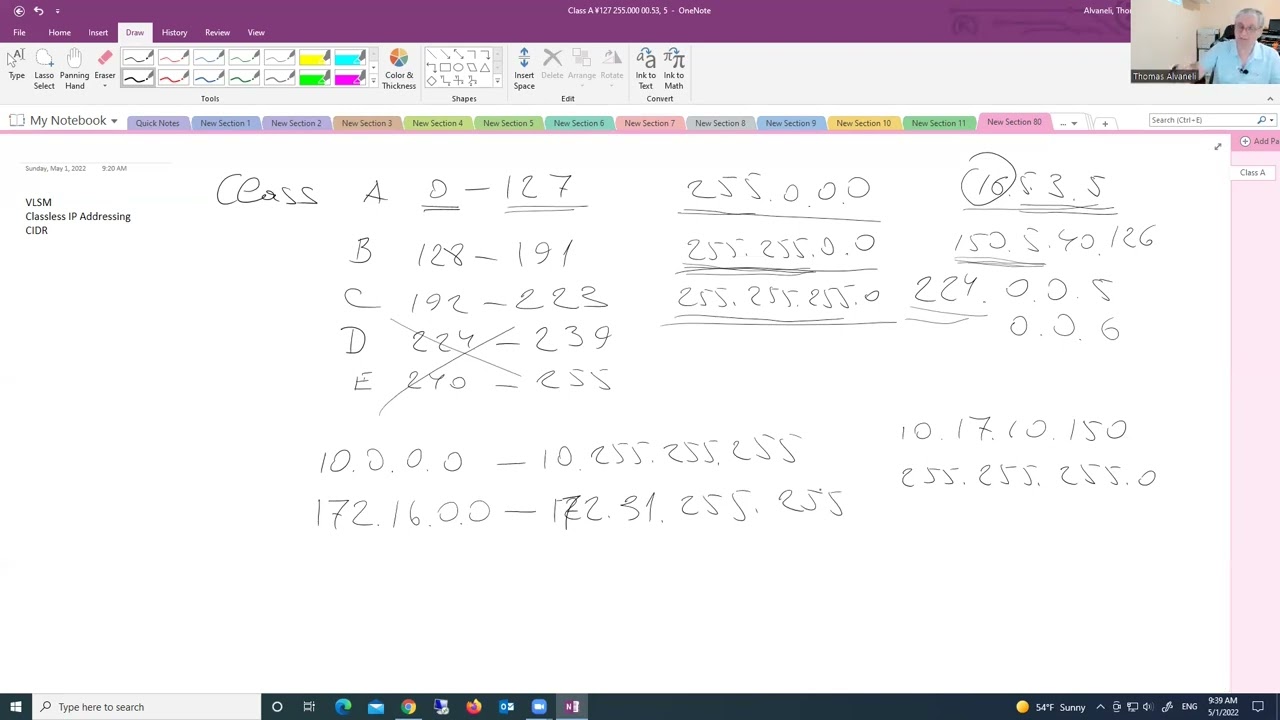
Subnet Mask Class To watch "classification of ipv4 addresses part 1. This program takes an ip address in classful notation as input (e.g. 192.168.0.0) and converts it to classless addressing (cidr notation) by checking the class of the ip address and setting the mask (number after '/') on that basis.

Network / Subnet Mask, Network, Broadcast Ip Hesaplama
Network / Subnet Mask, Network, Broadcast Ip Hesaplama This article gives a brief introduction on ipv4, public and private addresses, how the ip address is broken down and how subnetting occurs. find a complete introductory guide on routing and switching in our ubiquiti broadband routing & switching specialist (ubrss) guide, downloadable in our training section. back to top. To understand this, we must look at the devices' unique ip addresses as well as the associated subnet mask and default gateway. with these three pieces of information, we know how a device communicates with others locally as well as across an entire network. Ip address space was depleting rapidly the internet engineering task force (ietf) introduced classless inter domain routing (cidr) cidr uses variable length subnet masking (vlsm) to help conserve address space. Every ip address must be accompanied by a subnet mask. by now you should be able to look at an ip address and tell what class it is. unfortunately your computer doesn’t think that way. for your computer to determine the network and subnet portion of an ip address it must “and” the ip address with the subnet mask. what you see 192 . 100 . 10 .

Understanding Classless Subnet Mask Ccna Hub - Vrogue.co
Understanding Classless Subnet Mask Ccna Hub - Vrogue.co Ip address space was depleting rapidly the internet engineering task force (ietf) introduced classless inter domain routing (cidr) cidr uses variable length subnet masking (vlsm) to help conserve address space. Every ip address must be accompanied by a subnet mask. by now you should be able to look at an ip address and tell what class it is. unfortunately your computer doesn’t think that way. for your computer to determine the network and subnet portion of an ip address it must “and” the ip address with the subnet mask. what you see 192 . 100 . 10 . Finally this chapter looks at some troubleshooting techniques that are used to solve ip address related problems. the two current versions of ip addresses in use today are ipv4 and ipv6. this chapter focuses on ipv4. ipv6 is discussed in chapter 12. Ip addressing is a fundamental concept in networking. this chapter covers the basics of ipv4 and ipv6, including how ip addresses work, the differences between private and public ip addresses, and the principles of subnetting. Describe the structure of an ipv4 address including the network portion, the host portion, and the subnet mask. compare the characteristics and uses of the unicast, broadcast, and multicast ipv4 addresses. Ip addresses and subnets are necessary for effective network communications. learn how ip addresses and subnets work, and compare classful and classless ip addresses. network devices use ip addresses and subnets to identify the source and destination of communications and manage network addresses respectively.

What Is The Subnet Mask Protocol At Mason Mullan Blog
What Is The Subnet Mask Protocol At Mason Mullan Blog Finally this chapter looks at some troubleshooting techniques that are used to solve ip address related problems. the two current versions of ip addresses in use today are ipv4 and ipv6. this chapter focuses on ipv4. ipv6 is discussed in chapter 12. Ip addressing is a fundamental concept in networking. this chapter covers the basics of ipv4 and ipv6, including how ip addresses work, the differences between private and public ip addresses, and the principles of subnetting. Describe the structure of an ipv4 address including the network portion, the host portion, and the subnet mask. compare the characteristics and uses of the unicast, broadcast, and multicast ipv4 addresses. Ip addresses and subnets are necessary for effective network communications. learn how ip addresses and subnets work, and compare classful and classless ip addresses. network devices use ip addresses and subnets to identify the source and destination of communications and manage network addresses respectively.

Routing Protocols And Concepts – Chapter 6 - Ppt Stáhnout
Routing Protocols And Concepts – Chapter 6 - Ppt Stáhnout Describe the structure of an ipv4 address including the network portion, the host portion, and the subnet mask. compare the characteristics and uses of the unicast, broadcast, and multicast ipv4 addresses. Ip addresses and subnets are necessary for effective network communications. learn how ip addresses and subnets work, and compare classful and classless ip addresses. network devices use ip addresses and subnets to identify the source and destination of communications and manage network addresses respectively.

Chapter 7: IP Addressing - Ppt Download
Chapter 7: IP Addressing - Ppt Download
Part 2 - IP subnet masks; Private and public IPv4 addresses; Classless IP addressing
Part 2 - IP subnet masks; Private and public IPv4 addresses; Classless IP addressing
Related image with part 2 ip subnet masks private and public ipv4 addresses classless ip addressing
Related image with part 2 ip subnet masks private and public ipv4 addresses classless ip addressing
About "Part 2 Ip Subnet Masks Private And Public Ipv4 Addresses Classless Ip Addressing"
















Comments are closed.