Ipv6 Global Unicast Address Structure

IPv6 Global Unicast Address Structure. | Download Scientific Diagram
IPv6 Global Unicast Address Structure. | Download Scientific Diagram This tutorial explains the structures and functions of the ipv6 unicast addresses in detail. learn how many types of unicast addresses are available in ipv6 and how each type works. In this lesson, we are going to look at all types of ipv6 addresses in the unicast, multicast, and anycast categories. we will examine the global unicast, both link local and unique local addresses, embedded ipv4, and some special types like the loopback and the unspecified address.

IPv6 Global Unicast Address Structure. | Download Scientific Diagram
IPv6 Global Unicast Address Structure. | Download Scientific Diagram Unicast addresses, anycast addresses, and multicast addresses, and an. ipv6 node's required addresses. this document obsoletes rfc 3513, "ip version 6 addressing. architecture". hinden standards track [page 1] 1. introduction . 2 2. This document obsoletes rfc 2374, "an ipv6 aggregatable global unicast address format". it defined an ipv6 address allocation structure that includes top level aggregator (tla) and next level aggregator (nla). this document makes rfc 2374 and the tla/nla structure historic. 1. introduction rfc 2374, "an ipv6 aggregatable global unicast address. Like ipv4, there are different ipv6 address types also in ipv6 world. here, we will focus on these ipv6 addresses and we will learn the details of these ipv6 address types. In this guide, we’ll explore the concept of ipv6 global unicast address, their structure, characteristics, and examples. you may also like to read ipv6 anycast implementation.

Global Unicast Address In CCNA | GeeksforGeeks
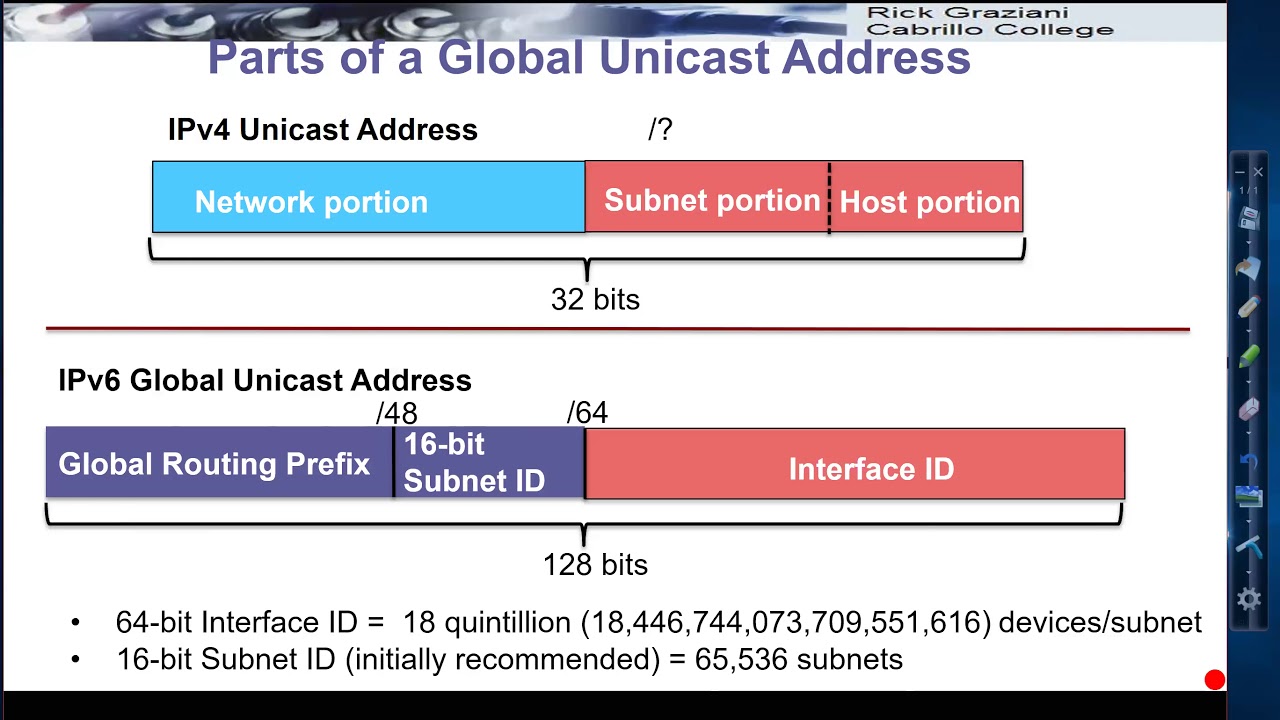
Global Unicast Address In CCNA | GeeksforGeeks Like ipv4, there are different ipv6 address types also in ipv6 world. here, we will focus on these ipv6 addresses and we will learn the details of these ipv6 address types. In this guide, we’ll explore the concept of ipv6 global unicast address, their structure, characteristics, and examples. you may also like to read ipv6 anycast implementation. To access cisco feature navigator, go to www.cisco.com/ go/ cfn. an account on cisco.com is not required. an ipv6 unicast address is an identifier for a single interface, on a single node. a packet that is sent to a unicast address is delivered to the interface identified by that address. At the heart of ipv6's enhancements is the concept of global unicast addresses (guas), a cornerstone for achieving expansive, worldwide connectivity. these addresses are not merely numerical tags but pivotal elements that ensure the internet remains an inclusive, global network. Key concept: the part of the ipv6 address space set aside for unicast addresses is structured into an address format that uses the first 48 bits for the routing prefix (like a network id), the next 16 bits for a subnet id, and the final 64 bits for an interface id (like a host id). Figure 2 shows the structure of a global unicast address using a /48 global routing prefix. /48 prefixes are the most common global routing prefixes assigned and will be used in most of the examples throughout this course.

My Journey To CCIE: IPv6 Global Unicast Address
My Journey To CCIE: IPv6 Global Unicast Address To access cisco feature navigator, go to www.cisco.com/ go/ cfn. an account on cisco.com is not required. an ipv6 unicast address is an identifier for a single interface, on a single node. a packet that is sent to a unicast address is delivered to the interface identified by that address. At the heart of ipv6's enhancements is the concept of global unicast addresses (guas), a cornerstone for achieving expansive, worldwide connectivity. these addresses are not merely numerical tags but pivotal elements that ensure the internet remains an inclusive, global network. Key concept: the part of the ipv6 address space set aside for unicast addresses is structured into an address format that uses the first 48 bits for the routing prefix (like a network id), the next 16 bits for a subnet id, and the final 64 bits for an interface id (like a host id). Figure 2 shows the structure of a global unicast address using a /48 global routing prefix. /48 prefixes are the most common global routing prefixes assigned and will be used in most of the examples throughout this course.

IPv6 Global Unicast Address ⋆ | IPv6 Address Types Global Unicast
IPv6 Global Unicast Address ⋆ | IPv6 Address Types Global Unicast Key concept: the part of the ipv6 address space set aside for unicast addresses is structured into an address format that uses the first 48 bits for the routing prefix (like a network id), the next 16 bits for a subnet id, and the final 64 bits for an interface id (like a host id). Figure 2 shows the structure of a global unicast address using a /48 global routing prefix. /48 prefixes are the most common global routing prefixes assigned and will be used in most of the examples throughout this course.
IPv6 Global Unicast Address
IPv6 Global Unicast Address
Related image with ipv6 global unicast address structure
Related image with ipv6 global unicast address structure
About "Ipv6 Global Unicast Address Structure"
















Comments are closed.