Force Vectors And Vector Components In 11 Minutes Statics

Force Vectors (Static) | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Cartesian Coordinate System
Force Vectors (Static) | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Cartesian Coordinate System Because the magnitude and direction of a force are both important, force is a vector quantity (force vector). the si unit of force is the newton (n), and force is often represented by the symbol f. Force, in mechanics, any action that tends to maintain or alter the motion of a body or to distort it. the concept of force is commonly explained in terms of isaac newton’s three laws of motion. because force has both magnitude and direction, it is a vector quantity.

Lecture Statics - Part 1 - Resultant Of Force Systems | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Force
Lecture Statics - Part 1 - Resultant Of Force Systems | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Force The force on an object equals the object’s mass multiplied by its acceleration. when one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first. Terms like stretch and squeeze can also be used to denote force. in physics, force is defined as: the push or pull on an object with mass causes it to change its velocity. force is an external agent capable of changing a body’s state of rest or motion. it has a magnitude and a direction. At its core, a force is an interaction that changes the motion of an object. it’s not something you can hold in your hand, but it has real, observable effects. A force is a power that causes an object to move or that changes movement.

Statics - Presentation | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Force
Statics - Presentation | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Force At its core, a force is an interaction that changes the motion of an object. it’s not something you can hold in your hand, but it has real, observable effects. A force is a power that causes an object to move or that changes movement. A force is a push or pull that acts upon an object as a result of that objects interactions with its surroundings. in this lesson, the physics classroom differentiates between the various types of forces that an object could encounter. Force is the "push" or "pull" exerted on an object to make it move or accelerate. newton's second law of motion describes how force is related to mass and acceleration, and this relationship is used to calculate force. in general, the. When we push or pull on a body, we are said to exert a force on it. forces can also be exerted by inanimate objects. for example, a locomotive exerts a force on a train it is pulling or pushing. similarly, compressed air in a container exerts a force on the wall of the container. A force is something that causes a change in the motion or shape of an object. in other words, a force can have one or more of the following effects on an object:.

Moments Of Forces: Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Statics | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Force
Moments Of Forces: Vector Mechanics For Engineers: Statics | PDF | Euclidean Vector | Force A force is a push or pull that acts upon an object as a result of that objects interactions with its surroundings. in this lesson, the physics classroom differentiates between the various types of forces that an object could encounter. Force is the "push" or "pull" exerted on an object to make it move or accelerate. newton's second law of motion describes how force is related to mass and acceleration, and this relationship is used to calculate force. in general, the. When we push or pull on a body, we are said to exert a force on it. forces can also be exerted by inanimate objects. for example, a locomotive exerts a force on a train it is pulling or pushing. similarly, compressed air in a container exerts a force on the wall of the container. A force is something that causes a change in the motion or shape of an object. in other words, a force can have one or more of the following effects on an object:.

Forces - Vectors And Moments | PDF | Pressure | Force
Forces - Vectors And Moments | PDF | Pressure | Force When we push or pull on a body, we are said to exert a force on it. forces can also be exerted by inanimate objects. for example, a locomotive exerts a force on a train it is pulling or pushing. similarly, compressed air in a container exerts a force on the wall of the container. A force is something that causes a change in the motion or shape of an object. in other words, a force can have one or more of the following effects on an object:.
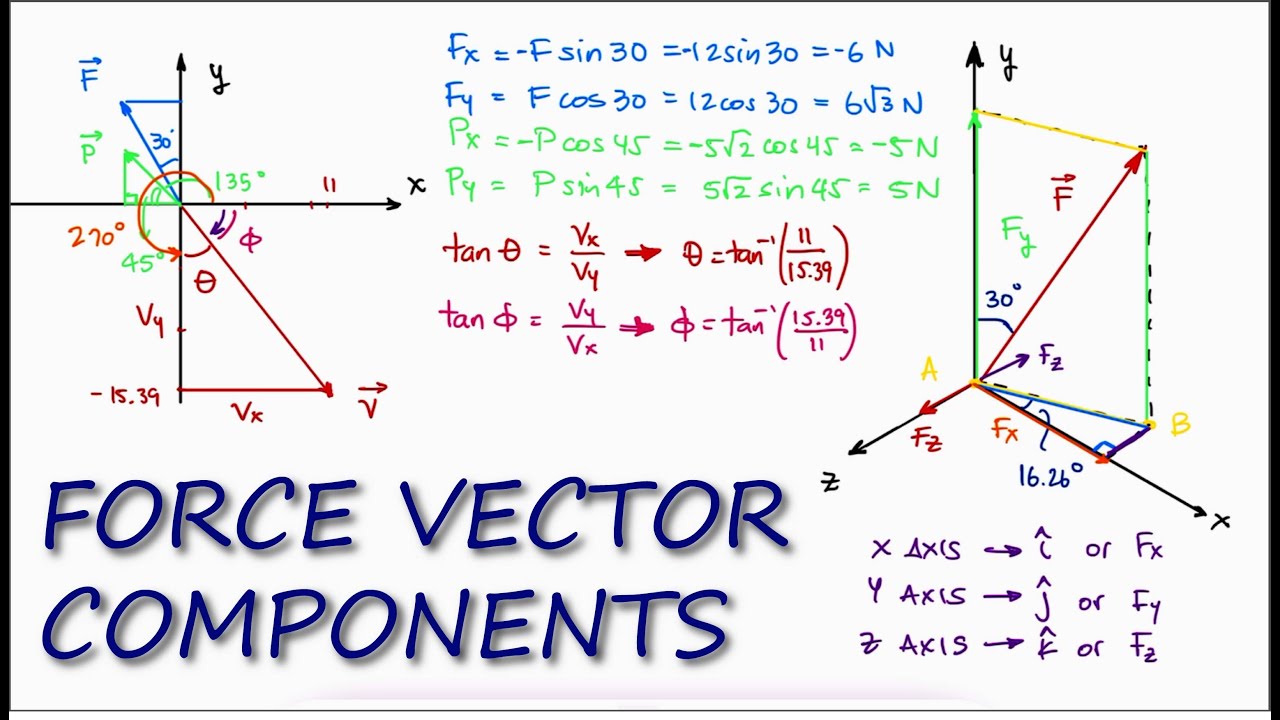
Force Vectors and VECTOR COMPONENTS in 11 Minutes! - STATICS
Force Vectors and VECTOR COMPONENTS in 11 Minutes! - STATICS
Related image with force vectors and vector components in 11 minutes statics
Related image with force vectors and vector components in 11 minutes statics
About "Force Vectors And Vector Components In 11 Minutes Statics"
















Comments are closed.